Research Highlights
2020
| Title | Evidence of Spin-Orbital Angular Momentum Interactions in Relativistic Heavy-Ion Collisions |
|---|
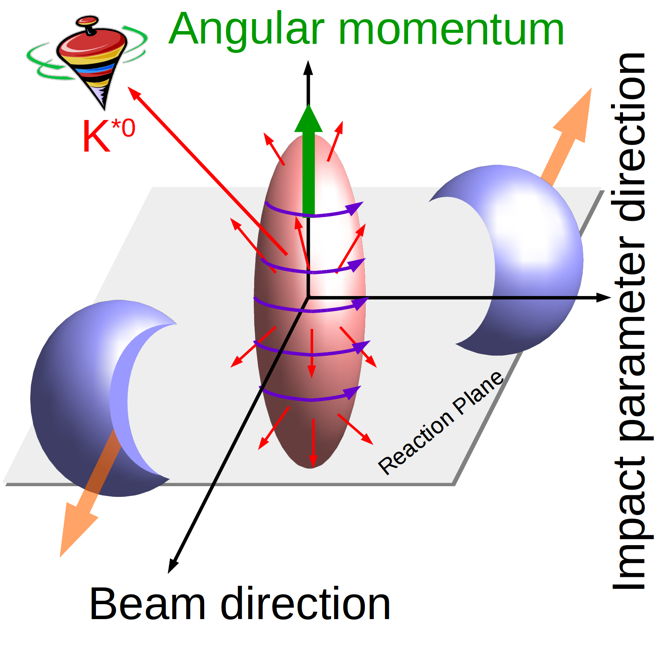 For the first time, evidence has been found for a significant spin alignment of vector mesons in
heavy-ion collisions. The effect is strongest at low pT with respect to a vector perpendicular to
the reaction plane and for midcentral (10–50%) collisions. These observations are qualitatively
consistent with expectations from the effect of large initial angular momentum in noncentral
heavy-ion collisions, which leads to quark polarization via spin-orbit coupling, subsequently
transferred to hadronic degrees of freedom by hadronization via recombination.
For the first time, evidence has been found for a significant spin alignment of vector mesons in
heavy-ion collisions. The effect is strongest at low pT with respect to a vector perpendicular to
the reaction plane and for midcentral (10–50%) collisions. These observations are qualitatively
consistent with expectations from the effect of large initial angular momentum in noncentral
heavy-ion collisions, which leads to quark polarization via spin-orbit coupling, subsequently
transferred to hadronic degrees of freedom by hadronization via recombination.
| Journal | Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 012301 (2020) |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | ALICE |
| Full list of primary authors | Ajay Kumar Dash, Sourav Kundu, Bedangadas Mohanty, Ranbir Singh |
| Primary author institutes | NISER |
| News |
|
2017
| Title | Bulk Properties of the Medium Produced in Relativistic Heavy-Ion Collisions from the Beam Energy Scan Program |
|---|
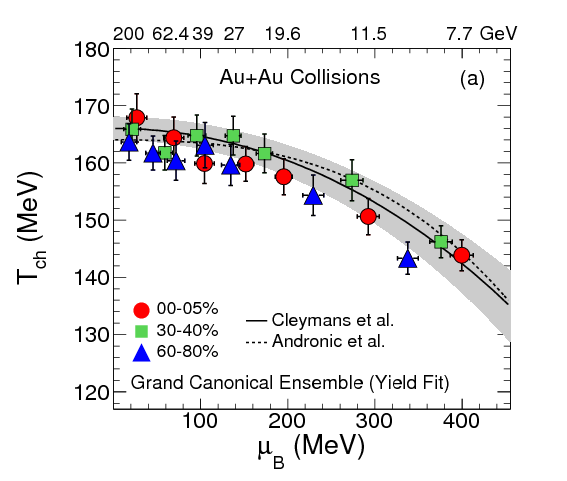 We have studied the bulk properties of matter in the Beam Energy Scan program (BES) at RHIC. The BES
program covers the energy range from 7.7 GeV to 39 GeV which along with top RHIC energy corresponds
to the baryon chemical potential region of 20-400 MeV. The mid-rapidity yields of identified hadrons
have been presented. They show the expected signatures of a high-baryon stopping region at lower
energies. At high energies, the pair production mechanism dominates the particle production. At
intermediate energies there is clearly a transition between these two regions, which is explored by
the BES Program. The data have been used to analyse both chemical and kinetic freeze-out parameters.
The results indicate in heavy-ion collisions a clear centrality dependence of the baryon chemical
potential at lower energies. The centrality dependence of the freeze-out parameters provides an
opportunity for the BES program at RHIC to enlarge the \((T, \mu_B)\) region of the phase diagram to
search for the QCD critical point. The difference between chemical and kinetic freeze-out increases
with increasing energy suggesting increasing hadronic interactions after chemical freeze-out at
higher energies.
We have studied the bulk properties of matter in the Beam Energy Scan program (BES) at RHIC. The BES
program covers the energy range from 7.7 GeV to 39 GeV which along with top RHIC energy corresponds
to the baryon chemical potential region of 20-400 MeV. The mid-rapidity yields of identified hadrons
have been presented. They show the expected signatures of a high-baryon stopping region at lower
energies. At high energies, the pair production mechanism dominates the particle production. At
intermediate energies there is clearly a transition between these two regions, which is explored by
the BES Program. The data have been used to analyse both chemical and kinetic freeze-out parameters.
The results indicate in heavy-ion collisions a clear centrality dependence of the baryon chemical
potential at lower energies. The centrality dependence of the freeze-out parameters provides an
opportunity for the BES program at RHIC to enlarge the \((T, \mu_B)\) region of the phase diagram to
search for the QCD critical point. The difference between chemical and kinetic freeze-out increases
with increasing energy suggesting increasing hadronic interactions after chemical freeze-out at
higher energies.
| Journal | Phys. Rev. C 96, 044904 – Published 13 October 2017 |
|---|---|
| Citations | 275+ |
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | Sabita Das, Declan Keane, Lokesh Kumar, Bedangadas Mohanty |
| Primary author institutes | IOP, Kent State University, Panjab University, NISER |
| News |
|
2016
| Title | Bulk Properties of the Medium Produced in Relativistic Heavy-Ion Collisions from the Beam Energy Scan Program |
|---|
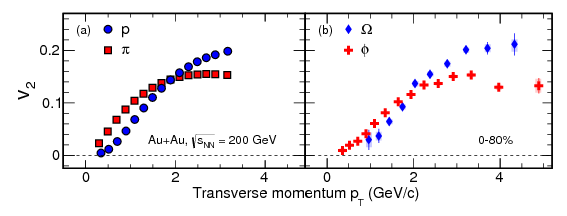 We have reported high-statistics elliptic flow measurements for multi-strange hadrons (\(\Sigma\)
and \(\Omega\)) and
\(\phi\) meson with other light and strange hadrons \((\pi,K,K^0_S,p\) and \(\Lambda)\) in Au + Au
collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}= 200\) GeV
for different centralities. The \(p_T\) dependence of \(\phi\) and \(\Omega\) \(v_2\) is observed to
be similar to that of \(\pi\)
and \(p\), indicating that a large amount of collectivity is developed in the initial partonic phase
for
light and strange hadrons. NCQ scaling holds within the statistical uncertainty for both 0-30% and
30-80% centralities, suggesting collective motion of quarks prior to hadronization.
We have reported high-statistics elliptic flow measurements for multi-strange hadrons (\(\Sigma\)
and \(\Omega\)) and
\(\phi\) meson with other light and strange hadrons \((\pi,K,K^0_S,p\) and \(\Lambda)\) in Au + Au
collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}= 200\) GeV
for different centralities. The \(p_T\) dependence of \(\phi\) and \(\Omega\) \(v_2\) is observed to
be similar to that of \(\pi\)
and \(p\), indicating that a large amount of collectivity is developed in the initial partonic phase
for
light and strange hadrons. NCQ scaling holds within the statistical uncertainty for both 0-30% and
30-80% centralities, suggesting collective motion of quarks prior to hadronization.
| Journal | Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 062301 – Published 10 February 2016 |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | Hiroshi Masui, Bedangadas Mohanty, Md. Nasim, Shusu Shi, Xu Sun |
| Primary author institutes | LBNL, NISER, CCNU |
| Corresponding author | Md. Nasim (NISER) |
| Title | \(K^{∗0}(892)\) and \(\phi(1020)\) production in Pb-Pb collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=2.76\) TeV |
|---|
 The \(K^*\) yields relative to charged kaons in Pb-Pb collisions show a suppression with respect to
pp
collisions, which increases with the system size. In contrast, no such suppression is observed for
the \(\phi\) mesons. The lack of suppression for the \(\phi\) meson can be attributed to the fact
that most of
them decay outside the fireball because of its longer lifetime (\(46.3 \pm 0.4\) fm/c). Because of a
shorter lifetime (\(K^* = 4.16 \pm 0.05\) fm/c), a significant number of produced \(K^*\) decays in
the
hadronic
medium. The decay product(s) undergo interactions with other hadrons in the medium resulting in a
significant change in their momentum, and no longer contributing to the \(K^*\) signal reconstructed
in
the experiment. Although both rescattering and regeneration are possible, the results presented here
represent an experimental demonstration of the predominance of rescattering effects in the hadronic
phase of the system produced in heavy-ion collisions.
The \(K^*\) yields relative to charged kaons in Pb-Pb collisions show a suppression with respect to
pp
collisions, which increases with the system size. In contrast, no such suppression is observed for
the \(\phi\) mesons. The lack of suppression for the \(\phi\) meson can be attributed to the fact
that most of
them decay outside the fireball because of its longer lifetime (\(46.3 \pm 0.4\) fm/c). Because of a
shorter lifetime (\(K^* = 4.16 \pm 0.05\) fm/c), a significant number of produced \(K^*\) decays in
the
hadronic
medium. The decay product(s) undergo interactions with other hadrons in the medium resulting in a
significant change in their momentum, and no longer contributing to the \(K^*\) signal reconstructed
in
the experiment. Although both rescattering and regeneration are possible, the results presented here
represent an experimental demonstration of the predominance of rescattering effects in the hadronic
phase of the system produced in heavy-ion collisions.
| Journal | Phys. Rev. C 91, 024609 – Published 17 February 2015 |
|---|---|
| Citations | 230+ |
| Collaboration | ALICE |
| Full list of primary authors | Anders Knospe, Christina Markert, Bedangadas Mohanty, Subhash Singha (PhD thesis paper) |
| Primary author institutes | University of Texas, NISER |
2014
| Title | Energy Dependence of Moments of Net-proton Multiplicity Distributions at RHIC |
|---|
 We report the measurements of the higher moments and their products (Sσ and κσ2) of the net-proton
distributions at midrapidity \((|y|\lt 0.5)\) within \(0.4\lt p_T \lt 0.8GeV\) in Au+Au collisions
over a wide range
of \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}\) and \(\mu_B\) have been presented to search for a possible Critical
Point (CP) and signals of a
phase transition in the collisions. These observables show a centrality and energy dependence,
which are neither reproduced by non-CP transport model calculations, nor by a hadron resonance
gas model. For \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}\gt 39\) GeV, \(S\sigma\) and \(\kappa\sigma^2\) values are
simi-lar for central, peripheral Au+Au
collisions and p+p collisions. Deviations for both \(\kappa\sigma^2\) and \(S\sigma\) from HRG and
Skellam expectations
are observed for \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}\leq 27\) GeV. The data presented here also provides
information to extract
freeze-out conditions in heavy-ion collisions using QCD based approaches .
We report the measurements of the higher moments and their products (Sσ and κσ2) of the net-proton
distributions at midrapidity \((|y|\lt 0.5)\) within \(0.4\lt p_T \lt 0.8GeV\) in Au+Au collisions
over a wide range
of \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}\) and \(\mu_B\) have been presented to search for a possible Critical
Point (CP) and signals of a
phase transition in the collisions. These observables show a centrality and energy dependence,
which are neither reproduced by non-CP transport model calculations, nor by a hadron resonance
gas model. For \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}\gt 39\) GeV, \(S\sigma\) and \(\kappa\sigma^2\) values are
simi-lar for central, peripheral Au+Au
collisions and p+p collisions. Deviations for both \(\kappa\sigma^2\) and \(S\sigma\) from HRG and
Skellam expectations
are observed for \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}\leq 27\) GeV. The data presented here also provides
information to extract
freeze-out conditions in heavy-ion collisions using QCD based approaches .
| Journal | Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 032302 – Published 23 January 2014 |
|---|---|
| Citations | 440+ |
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | Lizhu Chen, Bill Llope, Xiaofeng Luo, Bedanga Mohanty, Daniel McDonald |
| Primary author institutes | CCNU, Wayne State University, Rice University, NISER |
| Coresponding author | Bedangadas Mohanty (NISER) |
| Title | Beam Energy Dependence of Moments of the Net-Charge Multiplicity Distributions in Au+Au Collisions at RHIC |
|---|
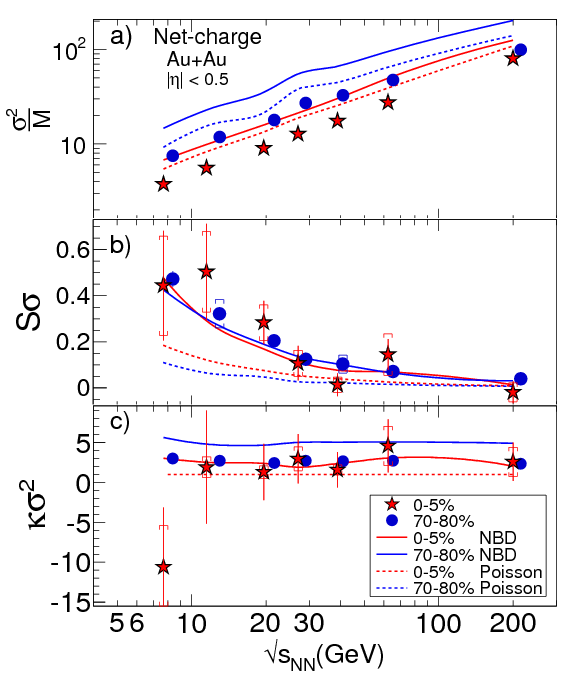 We report the first results of the moments of net-charge multiplicity distributions for\(|\eta|\lt
0.5\) as a
function of centrality for Au+Au collisions at seven collision energies from
\(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=7.7\) to \(200\) GeV
are presented. These data can be used to explore the nature of the QCD phase transition and to
locate the QCD critical point. The measured moments of net-charge multiplicity distributions
provide unique information about the freeze-out parameters by directly comparing with
theoretical model calculations. Future measurements with high statistics data will be needed for
precise determination of freeze-out conditions and to make definitive conclusions regarding the
critical point.
We report the first results of the moments of net-charge multiplicity distributions for\(|\eta|\lt
0.5\) as a
function of centrality for Au+Au collisions at seven collision energies from
\(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=7.7\) to \(200\) GeV
are presented. These data can be used to explore the nature of the QCD phase transition and to
locate the QCD critical point. The measured moments of net-charge multiplicity distributions
provide unique information about the freeze-out parameters by directly comparing with
theoretical model calculations. Future measurements with high statistics data will be needed for
precise determination of freeze-out conditions and to make definitive conclusions regarding the
critical point.
| Journal | Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 092301 – Published 26 August 2014 |
|---|---|
| Citations | 300+ |
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | W. J. Llope, D. McDonald, Bedangadas Mohanty, T. K. Nayak, N. R. Sahoo, G. Westfall. |
| Primary author institutes | MSU, VECC, Rice University, NISER |
2013
| Title | Net-Charge Fluctuations in Pb-Pb collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}} = 2.76\) TeV |
|---|
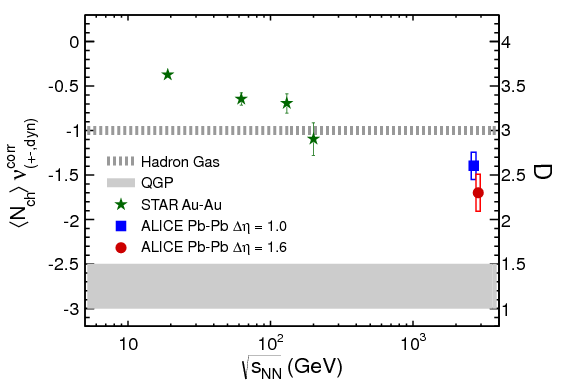 We report the first measurement of the net-charge fluctuations in Pb-Pb collisions at
\(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}} = 2.76\)
TeV, measured with the ALICE detector at the CERN Large Hadron Collider. The dynamical fluctuations
per unit entropy are observed to decrease when going from peripheral to central collisions. An
additional reduction in the amount of fluctuations is seen in comparison to the results from lower
energies. We examine the dependence of fluctuations on the pseudorapidity interval, which may
account for the dilution of fluctuations during the evolution of the system. We find that the
fluctuations at the LHC are smaller compared to the measurements at the BNL Relativistic Heavy Ion
Collider, and as such, closer to what has been theoretically predicted for the formation of a
quark-gluon plasma.
We report the first measurement of the net-charge fluctuations in Pb-Pb collisions at
\(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}} = 2.76\)
TeV, measured with the ALICE detector at the CERN Large Hadron Collider. The dynamical fluctuations
per unit entropy are observed to decrease when going from peripheral to central collisions. An
additional reduction in the amount of fluctuations is seen in comparison to the results from lower
energies. We examine the dependence of fluctuations on the pseudorapidity interval, which may
account for the dilution of fluctuations during the evolution of the system. We find that the
fluctuations at the LHC are smaller compared to the measurements at the BNL Relativistic Heavy Ion
Collider, and as such, closer to what has been theoretically predicted for the formation of a
quark-gluon plasma.
| Journal | Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 152301 – Published 10 April 2013 |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | ALICE |
| Full list of primary authors | Panagiotis Christakoglou, Tapan Nayak, Satyajit Jena, Basanta Nandi |
| Primary author institutes | NIKHEF, VECC, IIT-B |
| Title | Observation of an Energy-Dependent Difference in Elliptic Flow between Particles and Antiparticles in Relativistic Heavy Ion Collisions |
|---|
 We report the first observation of a beam-energy-dependent difference in elliptic flow versus
transverse momentum between particles and corresponding antiparticles for minimum bias
\(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=
7.7-62.4\) GeV Au+Au collisions at midrapidity. The difference increases with decreasing beam
energy.
Baryons show a larger difference compared to mesons. The relative values of \(v_2\) for charged
pions
have the opposite trend to the values of charged kaons. It is concluded that, at the lower energies,
particles and anti-particles are no longer consistent with the single NCQ scaling that was observed
for \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=200\) GeV. However, for the group of particles the NCQ scaling holds
within 10% while for the
group of antiparticles the difference between baryon and meso \(v_2\) continues to decrease to lower
energies. We further observed that the phi‑meson v2 atthe highest measured mT-m0 value is low
compared to other hadrons at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=7.7\)and \(11.5\) GeV with \(1.8\sigma\) and
\(2.3\sigma\), respectively.
We report the first observation of a beam-energy-dependent difference in elliptic flow versus
transverse momentum between particles and corresponding antiparticles for minimum bias
\(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=
7.7-62.4\) GeV Au+Au collisions at midrapidity. The difference increases with decreasing beam
energy.
Baryons show a larger difference compared to mesons. The relative values of \(v_2\) for charged
pions
have the opposite trend to the values of charged kaons. It is concluded that, at the lower energies,
particles and anti-particles are no longer consistent with the single NCQ scaling that was observed
for \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=200\) GeV. However, for the group of particles the NCQ scaling holds
within 10% while for the
group of antiparticles the difference between baryon and meso \(v_2\) continues to decrease to lower
energies. We further observed that the phi‑meson v2 atthe highest measured mT-m0 value is low
compared to other hadrons at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=7.7\)and \(11.5\) GeV with \(1.8\sigma\) and
\(2.3\sigma\), respectively.
| Journal | Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 142301 – Published 2 April 2013 |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | Xin Dong, Chitrasen Jena, Hiroshi Masui, Bedanga Mohanty, Md Nasim, Art Poskanzer, Hans Georg Ritter, Alex Schmah, Shusu Shi, Xiaoping Zhang, Jie Zhao |
| Primary author institutes | LBNL, NISER, IOP, VECC, CCNU, TU |
2011
| Title | Observation of the antimatter helium-4 nucleus |
|---|

High-energy nuclear collisions create an energy density similar to that of the Universe microseconds after the Big Bang; in both cases, matter and antimatter are formed with comparable abundance. However, the relatively short-lived expansion in nuclear collisions allows antimatter to decouple quickly from matter, and avoid annihilation. Thus, a high-energy accelerator of heavy nuclei provides an efficient means of producing and studying antimatter. The antimatter helium-4 nucleus (\(\bar{^4\mathrm{He}}\)), also known as the anti-\(\alpha\) (\(\bar{\alpha}\)), consists of two antiprotons and two antineutrons (baryon number B = −4). It has not been observed previously, although the α-particle was identified a century ago by Rutherford and is present in cosmic radiation at the ten per cent level. Antimatter nuclei with \(B \lt −1\) have been observed only as rare products of interactions at particle accelerators, where the rate of antinucleus production in high-energy collisions decreases by a factor of about 1,000 with each additional antinucleon. Here we report the observation of \(\bar{^4\mathrm{He}}\), the heaviest observed antinucleus to date. In total, 18 \(\bar{^4\mathrm{He}}\) counts were detected at the STAR experiment at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) in \(10^9\) recorded gold-on-gold (Au+Au) collisions at centre-of-mass energies of 200 GeV and 62 GeV per nucleon–nucleon pair. The yield is consistent with expectations from thermodynamic and coalescent nucleosynthesis models, providing an indication of the production rate of even heavier antimatter nuclei and a benchmark for possible future observations of \(\bar{^4\mathrm{He}}\) in cosmic radiation.
| Journal | Nature 473 (2011) 353 – Published 24 April 2011 |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | J. Chen, H. Crawford, Y. Fisyak, F. Geurts, Q. Hao, B. Huang , C. Jena, H. Ke, D. Keane, T. Kollegger, J. Landgraf, T. Ljubicic, M. Naglis, X. Sun, A. Tang, G. Van Buren, Z. Xu , L. Xue, J. Zhao. |
| Primary author institutes | LBNL, UCB, SNIP, Rice University, BNL, VECC, IOP, KSU |
| Chair of paper committee | Bedangadas Mohanty (VECC) |
2010
| Title | Identified particle production, azimuthal anisotropy, and interferometry measurements in Au+Au collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=9.2\) GeV |
|---|
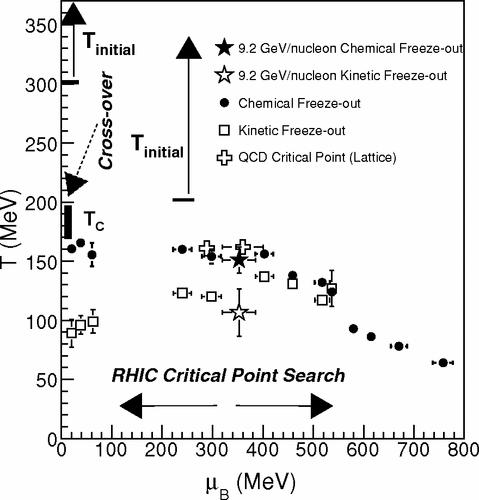 We present the first measurements of identified hadron production, azimuthal anisotropy, and pion
interferometry from Au+Au collisions below the nominal injection energy at the Relativistic
Heavy-Ion Collider (RHIC) facility. The data were collected using the large acceptance STAR detector
at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=9.2\) GeV from a test run of the collider in the year 2008. Midrapidity
results on
multiplicity density (\(dN/dy\)) in rapidity (\(y\)), average transverse momentum, particle ratios,
elliptic
flow, and HBT radii are consistent with the corresponding results at similar
\(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}\) from fixed target
experiments. Directed flow measurements are presented for both midrapidity and forward rapidity
regions. Furthermore the collision centrality dependence of identified particle \(dN/dy\), mean
\(p_T\) , and
particle ratios are discussed. These results also demonstrate the readiness of the STAR detector to
undertake the proposed QCD critical point search and the exploration of the QCD phase diagram at
RHIC.
We present the first measurements of identified hadron production, azimuthal anisotropy, and pion
interferometry from Au+Au collisions below the nominal injection energy at the Relativistic
Heavy-Ion Collider (RHIC) facility. The data were collected using the large acceptance STAR detector
at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}=9.2\) GeV from a test run of the collider in the year 2008. Midrapidity
results on
multiplicity density (\(dN/dy\)) in rapidity (\(y\)), average transverse momentum, particle ratios,
elliptic
flow, and HBT radii are consistent with the corresponding results at similar
\(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}\) from fixed target
experiments. Directed flow measurements are presented for both midrapidity and forward rapidity
regions. Furthermore the collision centrality dependence of identified particle \(dN/dy\), mean
\(p_T\) , and
particle ratios are discussed. These results also demonstrate the readiness of the STAR detector to
undertake the proposed QCD critical point search and the exploration of the QCD phase diagram at
RHIC.
| Journal | Phys. Rev. C 81, 024911 – Published 26 February 2010 |
|---|---|
| Citation | 210+ |
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | Madan M. Aggarwal, Jiyaun Chen, Debasish Das, Lokesh Kumar, Hiroshi Masui , Bedanga Mohanty, Yadav Pandit and Shusu Shi |
| Primary author institutes | PU, VECC, PU, LBNL, KSU |
| Chair of paper committee | Bedangadas Mohanty (VECC/LBNL) |
2009
| Title | \(K/\pi\) Fluctuations at Relativistic Energies |
|---|
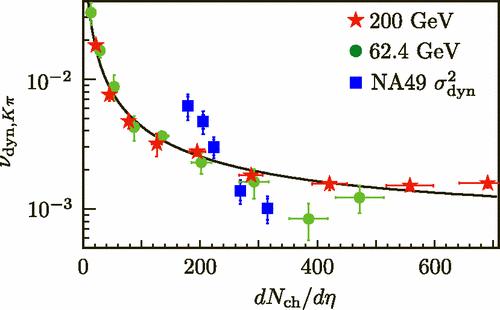 We report \(K/\pi\) fluctuations from Au+Au collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}= 19.6, 62.4, 130\)
and \(200\) GeV using the
STAR detector at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider. \(K/\pi\) fluctuations in central collisions
show
little dependence on incident energy and are on the same order as those from NA49 at the Super
Proton Synchrotron in central Pb+Pb collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}= 12.3\) and \(17.3\) GeV.
We report results for the
collision centrality dependence of \(K/\pi\) fluctuations and results for charge-separated
fluctuations.
We observe that the \(K/\pi\) fluctuations scale with the charged particle multiplicity density.
These
results may indicate that, due to later stage hadronic rescattering, the decay products of
resonances are less likely to survive in central collisions than in peripheral collisions, or may be
due to the onset of radial flow combined with our acceptance in \(p_T\).
We report \(K/\pi\) fluctuations from Au+Au collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}= 19.6, 62.4, 130\)
and \(200\) GeV using the
STAR detector at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider. \(K/\pi\) fluctuations in central collisions
show
little dependence on incident energy and are on the same order as those from NA49 at the Super
Proton Synchrotron in central Pb+Pb collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}= 12.3\) and \(17.3\) GeV.
We report results for the
collision centrality dependence of \(K/\pi\) fluctuations and results for charge-separated
fluctuations.
We observe that the \(K/\pi\) fluctuations scale with the charged particle multiplicity density.
These
results may indicate that, due to later stage hadronic rescattering, the decay products of
resonances are less likely to survive in central collisions than in peripheral collisions, or may be
due to the onset of radial flow combined with our acceptance in \(p_T\).
| Journal | Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 092301 – Published 24 August 2009 |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | G. Westfall, S. Das, S. Chattopadhyay, C. Pruneau, S. Voloshin, A. Vander Molen. |
| Primary author institutes | MSU, VECC, WSU |
2007
| Title | Energy dependence of \(\pi^\pm, p\) and anti-proton transverse momentum spectra for collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}} = 62.4\) and \(200\) GeV |
|---|
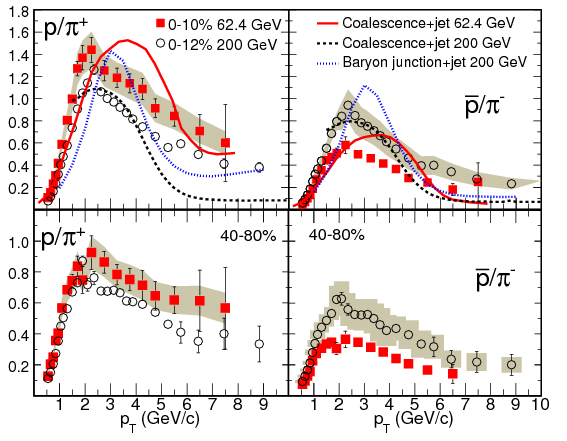 We have presented a study of the energy dependence of \(\pi^\pm, p\) and \(\bar{p}\) production for
Au+Au at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}} =
62.4\) and \(200\) GeV. These measurements provide new experimental data for investigating the
production
of quarks, gluons and their interactions with the medium formed in heavy-ioncollisions and the
interplay between coalescence of thermal partons and jet fragmentation.
We have presented a study of the energy dependence of \(\pi^\pm, p\) and \(\bar{p}\) production for
Au+Au at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}} =
62.4\) and \(200\) GeV. These measurements provide new experimental data for investigating the
production
of quarks, gluons and their interactions with the medium formed in heavy-ioncollisions and the
interplay between coalescence of thermal partons and jet fragmentation.
| Journal | Physics Letters B Volume 655, Issues 3–4, 1 November 2007, Pg 104-113 |
|---|---|
| Citations | 200+ |
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | Olga Barannikova, Haidong Liu, Pawan Kumar Netrakanti, Bedangadas Mohanty, Levente Molnar, Lijuan Ruan, Ming Shao, Zhangbu Xu |
| Primary author institutes | Purdue University, VECC, USTC, BNL |
| Corresponding author | Bedangadas Mohanty |
2006
| Title | Identified hadron spectra at large transverse momentum in p+p and d+Au collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}} = 200\) GeV |
|---|
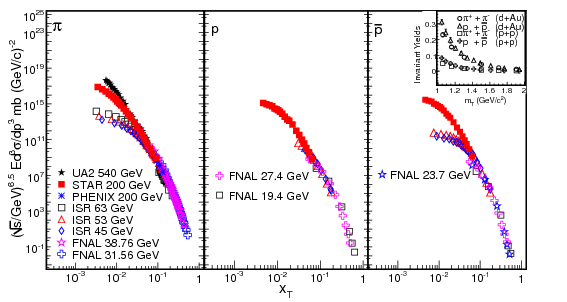 We have presented transverse momentum spectra for identified charged pions, protons and anti-protons
from p+p and d+Au collisions at√sNN= 200 GeV. The transverse momentum spectra are measured around
midrapidity \((|y|\lt 0.5)\) over the range of \(0.3 \lt pT \lt 10\) GeV/c with particle
identification from the
ionization energy loss and its relativistic rise in the Time ProjectionChamber, as well as the
Time-of-Flight in STAR. The following conclusions can be drawn from the present study: (a) The
nuclear modification factor around midrapidity is enhanced in d+Au collisions to about 1.5 for
pions and to about 2 for protons and antiprotons at intermediate \(p_T\) \((2 \lt p_T \lt5
GeV/c)\).(b)
Identified particle ratios are shown to be sensitive to the relative contributions from quark
and gluon fragmentation as well as to their fragmentation functions. (c) The NLOpQCD
calculations describe the high pT data for charged pions reasonably well in p+p collisions
and d+Au collisions. In general, baryon production has historically been difficult to describe by
pQCD and hadronization. (d) The proton and pion spectra in p+p collisions follow \(x_T\)-scaling
with
a beam-energy dependent factor \(\sim\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}6.5\) above \(p_T\sim 2\) GeV/c. The pion
and proton spectra follow
transverse mass scaling for \(m_T \lt 2\) GeV/\(c^2\) in both p+p and d+Au collisions, suggesting
the
transition region from soft to hard process domination occurs at \(p_T\sim 2\) GeV/c in these
collision
systems. The measurements presented in this paper provide better constraints on jet quenching
and quark recombination models which are presently the best candidates for explaining particle
production in the intermediate pT region.
We have presented transverse momentum spectra for identified charged pions, protons and anti-protons
from p+p and d+Au collisions at√sNN= 200 GeV. The transverse momentum spectra are measured around
midrapidity \((|y|\lt 0.5)\) over the range of \(0.3 \lt pT \lt 10\) GeV/c with particle
identification from the
ionization energy loss and its relativistic rise in the Time ProjectionChamber, as well as the
Time-of-Flight in STAR. The following conclusions can be drawn from the present study: (a) The
nuclear modification factor around midrapidity is enhanced in d+Au collisions to about 1.5 for
pions and to about 2 for protons and antiprotons at intermediate \(p_T\) \((2 \lt p_T \lt5
GeV/c)\).(b)
Identified particle ratios are shown to be sensitive to the relative contributions from quark
and gluon fragmentation as well as to their fragmentation functions. (c) The NLOpQCD
calculations describe the high pT data for charged pions reasonably well in p+p collisions
and d+Au collisions. In general, baryon production has historically been difficult to describe by
pQCD and hadronization. (d) The proton and pion spectra in p+p collisions follow \(x_T\)-scaling
with
a beam-energy dependent factor \(\sim\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}}6.5\) above \(p_T\sim 2\) GeV/c. The pion
and proton spectra follow
transverse mass scaling for \(m_T \lt 2\) GeV/\(c^2\) in both p+p and d+Au collisions, suggesting
the
transition region from soft to hard process domination occurs at \(p_T\sim 2\) GeV/c in these
collision
systems. The measurements presented in this paper provide better constraints on jet quenching
and quark recombination models which are presently the best candidates for explaining particle
production in the intermediate pT region.
| Journal | Physics Letters B Volume 637, Issue 3, 8 June 2006, Pg. 161-169 |
|---|---|
| Citations | 250+ |
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | Pawan K. Netrakanti, Bedangadas Mohanty, Zhangbu Xu |
| Primary author institutes | VECC, BNL |
| Corresponding author | Bedangadas Mohanty |
2005
| Title | Multiplicity and Pseudorapidity Distributions of Photons in Au+Au Collisions at \(\sqrt{s_\mathrm{NN}} = 62.4\) GeV |
|---|
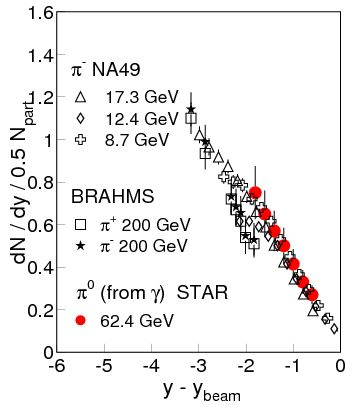 We have presented the first results of photon multiplicity measurements at RHIC in the
pseudorapidity region \(2.3\leq \eta\leq 3.7\). Photon production per participant pair is found to
be
approximately independent of centrality in this pseudorapidity region. Comparison with photon and
charged pion data at RHIC and SPS energies shows, for the first time in heavy ion collisions, that
photons and pions follow an energy independent limiting fragmentation behavior, as previously found
for inclusive charged particles. Furthermore, photons are observed to follow a centrality
independent limiting fragmentation scenario.
We have presented the first results of photon multiplicity measurements at RHIC in the
pseudorapidity region \(2.3\leq \eta\leq 3.7\). Photon production per participant pair is found to
be
approximately independent of centrality in this pseudorapidity region. Comparison with photon and
charged pion data at RHIC and SPS energies shows, for the first time in heavy ion collisions, that
photons and pions follow an energy independent limiting fragmentation behavior, as previously found
for inclusive charged particles. Furthermore, photons are observed to follow a centrality
independent limiting fragmentation scenario.
| Journal | Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 062301 – Published 5 August 2005 |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | STAR |
| Full list of primary authors | Pawan K. Netrakanti, Bedangadas Mohanty, Subhasis Chattopadhyay |
| Primary author institutes | VECC |
| Corresponding author | Bedangadas Mohanty |